Big Data UX
Establecer patrones de comportamiento que permitan alimentar sistemas de recomendación o adaptar el software a un público objetivo
Proyecto cofinanciado por el Fondo Europeo de Desarrollo Regional (FEDER) y la Sociedad para el Desarrollo Regional de Cantabria (SODERCAN) dentro del programa “I+C=+C 2016 – PROYECTOS I+D EN EL ÁMBITO DE LAS TIC, LÍNEA SMART”, con identificador de referencia TI16-IN-007.l 50%.

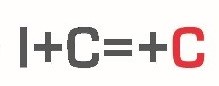
Introducción
Los entornos de computación ubicua son aquellos en los que la interacción con la tecnología ocurre en cualquier momento y lugar, a veces de manera invisible para el usuario, a través de cualquier tipo de dispositivo. Múltiples avances tecnológicos favorecen la aparición de estos entornos, como los relacionados con la domótica, los dispositivos portátiles o las ciudades inteligentes, además del enorme crecimiento en el uso de dispositivos portátiles como smartphones o tablets. Toda esta interacción produce grandes volúmenes de datos que pueden ser explotados para extraer y entender los hábitos y comportamientos del usuario. Y la adquisición de este conocimiento puede permitir que la tecnología evolucione según las necesidades del usuario.Contexto
Entre los muchos contextos ubicuos posibles, el más amplio y arraigado es el que surge de la interacción a través de smartphones y aplicaciones móviles (o apps). Estos dispositivos, ya en uso diario, recogen una cantidad de datos de diversa naturaleza, desde el uso de interfaces de usuario hasta los historiales de geolocalización o la interacción NFC (Near Field Communication). La información registrada tiene una riqueza versátil, de la cual se pueden extraer numerosos patrones de usabilidad, movilidad y preferencias, y con el potencial de informar sobre las características de una comunidad de usuarios, alimentar sistemas de recomendación o adaptar el software a un público objetivo. Sin embargo, se requiere un tratamiento especial para un descubrimiento efectivo del conocimiento debido a las altas dimensiones y al crecimiento constante de los datos.Objetivos del Proyecto
El objetivo de este proyecto es aprovechar los patrones de usuario que aparecen en estos entornos móviles. Para ello, se propone el uso de técnicas de aprendizaje automático y aprendizaje por observación (Learning From Observation) para la creación de modelos de comportamiento a partir del historial de interacciones. Los modelos, con capacidades predictivas y generativas, recogerán los patrones y particularidades del usuario y, posteriormente, permitirán, mediante aprendizaje no supervisado, segmentar una comunidad de usuarios en diferentes perfiles con una serie de comportamientos típicos. Con las técnicas desarrolladas, se desea obtener un sistema de software que genere especificaciones en lenguaje natural sobre los perfiles de usuario de una app. Las descripciones generadas proporcionarán una ventaja competitiva para ajustar los servicios y características de una app a su público o sus diferentes sectores, buscando así una mejora sustancial en la experiencia del usuario. Dentro de este marco, el usuario, a través de su actividad normal en una app, puede tener un papel mucho más significativo en su progreso.Nuestras oficinas en España
Encuentra la oficina más cercana a ti o escríbenos a atnaxpe@axpe.com
A Coruña
C/ Real, 74-76 15003
La Coruña
Tel: (+34) 915 901 960
Asturias
Parque Tecnológico Asturias,
Edificio Centroelena II, 2B,
33428 Llanera, Asturias
Tel: (+34) 984 498 079
Barcelona
Passeig de Gracia, 54, 6ª planta
08007, Barcelona
Tel: (+34) 932 411 463
Bilbao
Gran Vía de Don Diego López de Haro, 1,
48001 Bilbo,
Bizkaia
Cantabria
Polígono Camargo 16 39600,
Camargo (Cantabria)
Telf: (+34) 942 945 033
Madrid
C/ Arturo Soria, 122 28043,
Madrid
Tel: (+34) 915 901 960
C/ María de Portugal, 1, Planta 3ª,
CP 28050, Madrid
(Arktic)
Salamanca
C/ Toro, 76, 1ºd 37002
Salamanca
Tel: (+34) 915 901 960
Valladolid
Paseo Arco de Ladrillo, 92
47008, Valladolid
Tel: (+34) 983 548 063
Vitoria
Avenida de los Olmos, 1 01013,
Vitoria-Gasteiz
Tel: (+34) 945 359 705
Nuestras oficinas internacionales
Londres
Royds Withy King.
69 Carter Lane.
London. England
París
Patchwork Saint Lazare 3
Rue de Stockholm 75008 Paris,
Francia
Florida, USA
C/O Quest Workspaces One Biscayne Tower,
LLC 2S Biscayne Boulevard,
Suite 3200 Miami,
FL 33131