Big Data and sports: applications that are transforming the world.
For several years, we have been observing how Big Data is strongly impacting areas such as Marketing, Healthcare, Banking, and Insurance, but also in the world of professional sports. Nowadays, nearly everything is analyzed, from viewership ratings and fan attendance at stadiums to their demographics, such as origin, age, or gender, not to mention the specifics of the sport itself: distances covered, successful passes, points, strokes, etc. Additionally, athletes are continuously monitored, tracking real-time aspects such as vital signs, calories burned, and hours of sleep, among others, making the combination of Big Data and sports a perfect match.
The factor enabling these applications is the existence of increasingly sophisticated means to collect all this data (cameras, sensors, wearables, etc.) and the exponential growth in storage and processing capacity due to the emergence of new technologies. As a result, coaches can optimize the performance of their teams or athletes by improving their positioning on the field or refining technical details. They can also review the volume and type of training or adjust carbohydrate or protein intake based on the time of the season or the effort exerted to ensure proper recovery. The ultimate goal of combining Big Data and sports is to gather all this information to help professionals make the best decisions at every moment.

There are numerous examples of Big Data technology being used in some of the major sports around the world. In the United States, its use in basketball and baseball is already widespread. The NFL (National Football League) has a platform that supports all teams in the league by providing all types of information, from the condition of the playing surface to weather conditions and data from each player’s college stage.
Similarly, NBA (National Basketball Association) teams have real-time updated statistics that allow them to prepare strategies for each game, cameras that continuously track player movements, and vests that monitor health parameters. For instance, in 2013, the Golden State Warriors were the team with the most three-point attempts, so they installed a sophisticated camera system that essentially divides the court into a three-dimensional grid and records twenty images per second of each player to identify possible positioning errors.
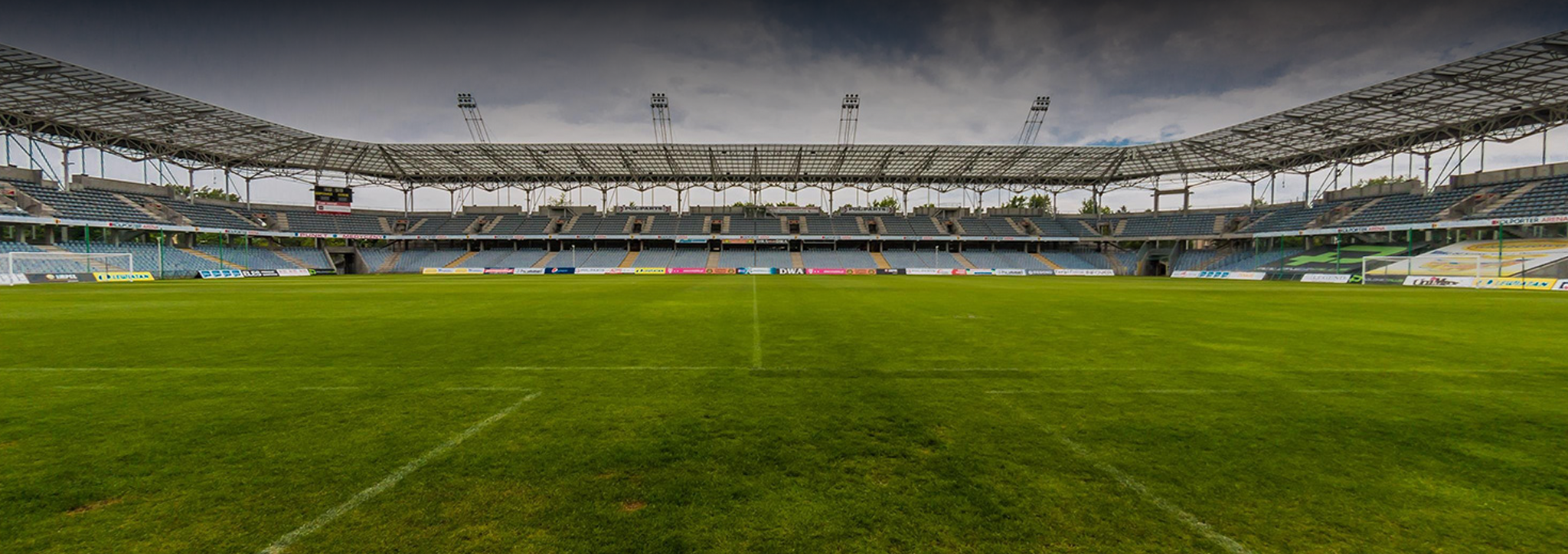
In Europe, the world of football has also experienced significant advancements in this field thanks to the combination of Big Data and sports. A notable example is the German national team during the 2014 World Cup. The use of sensors on players and cameras during training sessions and friendlies provided invaluable information to coach Joachim Löw and his staff, leading to their historic success: winning the championship.
At the club level, another example of Big Data in sports is Arsenal, which recently installed eight cameras in their stadium that continuously track their players to improve their positioning on the field. This innovative system collects 1.4 million data points per match and focuses on analyzing the moments when players are not in contact with the ball, their positioning, and their movements. A similar approach is being used by Barcelona in La Liga, which has implemented a system that allows them to better understand the playing patterns of rival teams and enhance their players’ movements.
In the English Premier League, Leicester City used Big Data techniques to address a serious issue. The season following their championship win (2015-2016), the team’s performance significantly declined, so they turned to a Big Data company to analyze, in the most objective way possible, the factors that had led to their success the previous year and, more importantly, what had changed in the following season to cause such a significant drop in the team’s results.

However, the use of Big Data in sports has numerous applications beyond improving performance and results. In contact sports like rugby or American football, coaching staff can make sports predictions, such as anticipating whether a player is at risk of injury, by comparing measurements provided by small sensors worn by players at all times with historical databases.
As mentioned at the beginning, the primary goal of utilizing Big Data in elite sports is to assist coaches and support staff in making the best decisions, ultimately enabling elite athletes to achieve maximum performance. In this regard, the possibilities for applying technology in sports are endless. This weekend, the 2018 World Cup in Russia has begun, and we are sure we will see novel and innovative ways to use Big Data for team preparation, so the technological revolution has only just begun!